Circular economy manufacturing is rapidly redefining how goods are designed, produced, and consumed in response to mounting environmental and economic pressures. Traditional manufacturing models followed a linear path of take, make, and dispose, resulting in excessive waste and resource depletion. Today, manufacturers are rethinking this approach by prioritizing waste reduction, extending product lifecycles through reuse, and embedding sustainable production principles into core operations. As global supply chains face volatility and regulatory scrutiny intensifies, circular economy manufacturing is emerging as a strategic framework that balances profitability with long-term resilience.
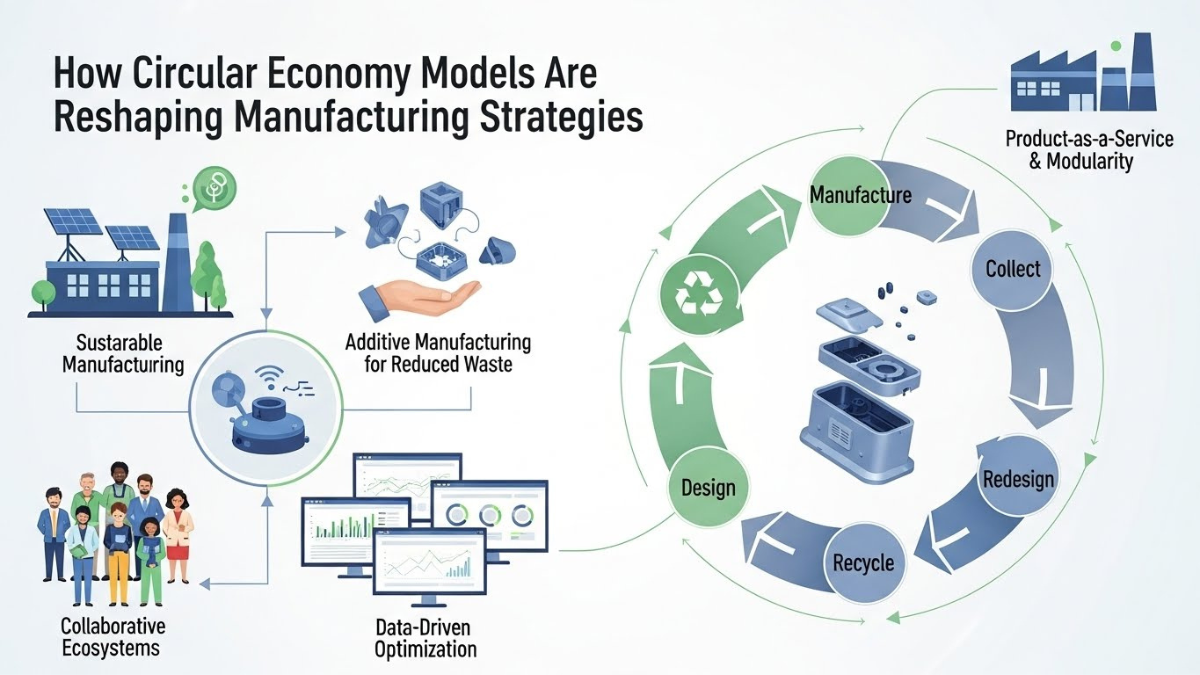
From Linear To Circular Manufacturing Models
The shift from linear systems to circular economy manufacturing represents a fundamental change in industrial thinking. Instead of viewing materials as disposable inputs, circular models treat them as valuable assets that can be recovered and reintegrated. This approach emphasizes waste reduction at every stage of production, from raw material sourcing to end-of-life management.
Manufacturers adopting circular strategies redesign products for durability, repairability, and reuse. Components are standardized, materials are selected for recyclability, and production processes are optimized to minimize waste. These changes support sustainable production by reducing dependence on virgin resources and lowering environmental impact. As industries face rising material costs, circular economy manufacturing also delivers economic advantages through efficiency and resource security.
Waste Reduction As A Strategic Priority
waste reduction is one of the most visible and impactful outcomes of circular economy manufacturing. By minimizing scrap, emissions, and byproducts, manufacturers lower disposal costs and regulatory risks. Advanced analytics and process optimization help identify inefficiencies, enabling continuous improvement across production lines.
Beyond operational benefits, waste reduction aligns with growing stakeholder expectations. Consumers, investors, and regulators increasingly demand transparency and accountability in manufacturing practices. Companies that demonstrate measurable progress toward waste reduction enhance brand reputation and market competitiveness. Within circular economy manufacturing, waste is no longer an unavoidable byproduct but a design flaw to be eliminated.
Reuse And Remanufacturing In Industrial Systems
Reuse plays a central role in circular economy manufacturing by extending the life of products and components. Remanufacturing, refurbishment, and parts recovery allow manufacturers to recapture value that would otherwise be lost. These practices reduce material demand while maintaining product quality and performance.
Industrial reuse also supports supply chain resilience. By recovering components internally, manufacturers reduce exposure to raw material shortages and price volatility. This closed-loop approach strengthens sustainable production by lowering energy consumption and emissions associated with extraction and processing. As technology advances, digital tracking and material passports further enhance the scalability of reuse within manufacturing ecosystems.
Sustainable Production And Design Innovation
Design innovation is essential to achieving sustainable production in circular economy manufacturing. Engineers and designers collaborate to create products that balance functionality, longevity, and environmental impact. Modular designs enable easy disassembly and reuse, while material innovation supports recyclability and reduced toxicity.
Sustainable production also extends to energy and water use. Manufacturers integrate renewable energy, closed-loop water systems, and low-impact processes to reduce environmental footprints. These investments often deliver long-term cost savings and compliance benefits. By embedding sustainability into design and operations, circular economy manufacturing transforms environmental responsibility into a driver of innovation.
Business Value And Competitive Advantage
Adopting circular economy manufacturing delivers tangible business value beyond environmental benefits. Cost savings from waste reduction, improved material efficiency, and enhanced asset utilization strengthen margins. New revenue streams emerge through service-based models, take-back programs, and refurbished products built on reuse.
From a strategic perspective, sustainable production enhances risk management and future-proofs operations against regulatory changes and resource scarcity. Companies that lead in circular practices attract talent, partners, and customers aligned with sustainability goals. As markets evolve, circular economy manufacturing becomes a source of differentiation and long-term competitiveness.
Implementation Challenges And Change Management
Transitioning to circular economy manufacturing is not without challenges. Legacy infrastructure, upfront investment costs, and organizational resistance can slow progress. Aligning suppliers and customers around reuse and waste reduction requires collaboration and clear incentives.
Successful implementation depends on leadership commitment and cross-functional integration. Training, data transparency, and performance metrics aligned with sustainable production goals help embed circular principles into daily operations. As best practices spread, shared standards and industry collaboration reduce barriers and accelerate adoption.
Key Strategies In Circular Economy Manufacturing
- Designing products for durability and reuse
- Prioritizing waste reduction through process optimization
- Integrating sustainable production technologies
- Establishing take-back and remanufacturing programs
- Collaborating across value chains
Table: Linear Manufacturing vs Circular Economy Manufacturing
| Aspect | Linear Manufacturing | Circular Economy Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Use | Single-use inputs | Continuous reuse |
| Waste | High disposal rates | Focus on waste reduction |
| Production Model | Take-make-dispose | Closed-loop sustainable production |
| Cost Structure | Volatile material costs | Improved efficiency |
| Environmental Impact | High | Reduced footprint |
Industry Examples And Sector Adoption
Multiple industries are embracing circular economy manufacturing to address sector-specific challenges. Automotive manufacturers remanufacture engines and components to support reuse. Electronics firms design devices for easy disassembly, reducing e-waste through waste reduction initiatives. Apparel companies adopt circular textiles to advance sustainable production.
These examples demonstrate scalability across complex supply chains. As digital tools improve traceability, manufacturers gain visibility into material flows, enabling more effective circular strategies. Industry collaboration accelerates learning and standardization, reinforcing the momentum behind circular economy manufacturing.
Measuring Impact And Performance
Measuring success in circular economy manufacturing requires new metrics beyond traditional output and cost indicators. Material circularity, recovery rates, and lifecycle emissions provide insights into waste reduction and sustainable production performance. Data-driven measurement supports accountability and continuous improvement.
Transparent reporting also builds trust with stakeholders. By communicating progress on reuse and circular goals, manufacturers demonstrate leadership and credibility. As reporting frameworks mature, benchmarking across industries further incentivizes adoption of circular economy manufacturing practices.
Conclusion
The rise of circular economy manufacturing marks a transformative shift in how industries create value while respecting environmental limits. By prioritizing waste reduction, enabling reuse, and embedding sustainable production into design and operations, manufacturers unlock efficiency, resilience, and innovation. While challenges remain, the long-term benefits of circular models are clear. As markets, regulations, and consumer expectations evolve, circular economy manufacturing will continue to reshape manufacturing strategies and define the future of industrial sustainability.
FAQs
What is circular economy manufacturing?
Circular economy manufacturing focuses on keeping materials in use through reuse, recycling, and efficient design.
How does waste reduction benefit manufacturers?
Waste reduction lowers costs, improves efficiency, and reduces environmental impact.
What role does reuse play in manufacturing?
Reuse extends product lifecycles and reduces reliance on new raw materials.
Is sustainable production expensive to implement?
While initial investment may be required, sustainable production often delivers long-term savings and resilience.
Which industries benefit most from circular economy manufacturing?
Automotive, electronics, apparel, and heavy manufacturing see strong benefits from circular economy manufacturing practices.
Click here to learn more